5.0 KiB
Xiaomi Mi Flora Plant Sensor MQTT Client/Daemon
A simple Linux python script to query arbitrary Mi Flora plant sensor devices and send the data to an MQTT broker, e.g., the famous Eclipse Mosquitto or the embedded MQTT broker in Home Assistant. After data made the hop to the MQTT broker it can be used by home automation software like Home Assistant or openHAB.
The program can be executed for a single run or in daemon mode to run continuously in the background.
Features
- Support for Xiaomi Mi Flora sensors (tested with firmware v2.6.2, v2.6.4, v2.6.6, v3.1.4, others anticipated)
- Build on top of open-homeautomation/miflora
- Highly configurable
- Data publication via MQTT
- JSON encoded
- MQTT authentication support
- Daemon mode (default)
- Systemd service file included, sd_notify messages generated
- MQTT-less mode, printing data directly to stdout/file
- Reliable and inituitive
- Tested on Raspberry Pi
Readings
The Mi Flora sensor offers the following plant and soil readings:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
temperature |
Air temperature, in [°C] (0.1°C resolution) |
light |
Sunlight intensity, in [lux] |
moisture |
(Soil moisture](https://observant.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/208067926-Monitoring-Soil-Moisture-for-Optimal-Crop-Growth), in [%] |
conductivity |
Soil fertility, in [µS/cm] |
battery |
Sensor battery level, in [%] |
Installation
On a modern Linux system just a few steps are needed. The following example shows the installation under Debian/Raspbian:
sudo apt install git python3 python3-pip bluetooth
git clone https://github.com/ThomDietrich/miflora-mqtt-daemon.git /opt/miflora-mqtt-daemon
cd /opt/miflora-mqtt-daemon
sudo pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Configuration
To match personal needs, all operation details can be configured using the file config.ini.
You need to add at least one sensor to the configuration. Scan for available Mi Flora sensors in your proximity with the command:
sudo hcitool lescan
Interfacing your Mi Flora sensor with this program is harmless. The device will not be modified and will still work with the official Xiaomi app.
Execution
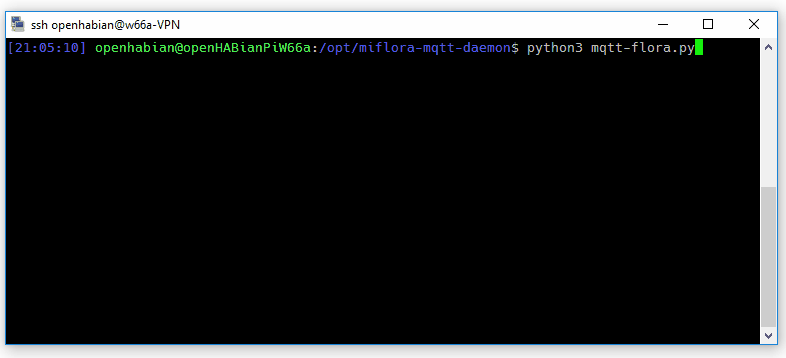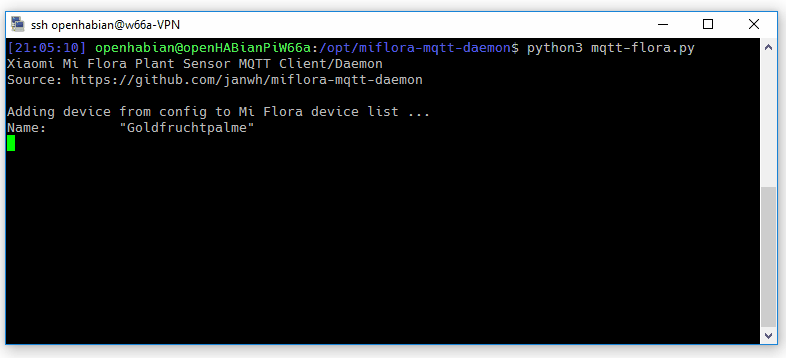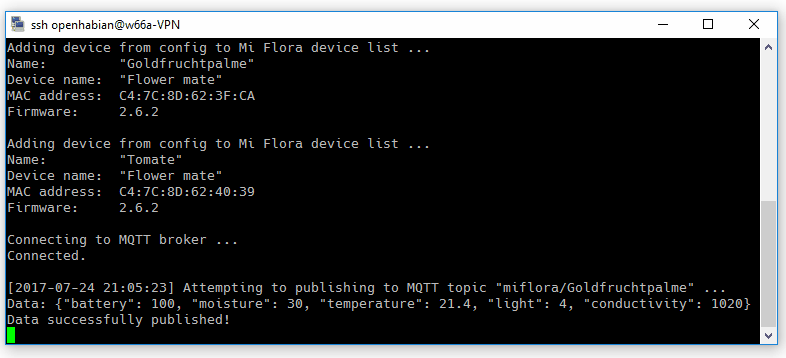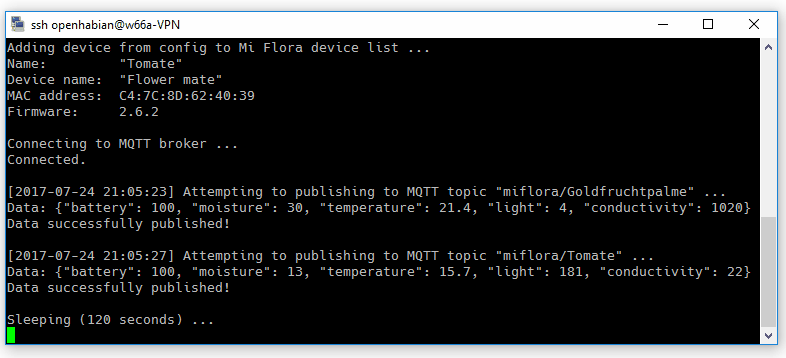
A first test run is as easy as:
python3 miflora-mqtt-daemon.py
With a correct configuration the result should look similar to the the screencap above. The extensive output can be reduced to error messages:
python3 miflora-mqtt-daemon.py > /dev/null
Continous Daemon/Service
You most probably want to execute the program continuously in the background. This can be done either by using the internal daemon or cron.
Attention: Daemon mode must be enabled in the configuration file (default).
-
Systemd service - on systemd powered systems the recommended option
sudo cp /opt/miflora-mqtt-daemon/template.service /etc/systemd/system/miflora.service sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start miflora.service sudo systemctl status miflora.service sudo systemctl enable miflora.service -
Screen Shell - Run the program inside a screen shell:
screen -S miflora-mqtt-daemon -d -m python3 /path/to/miflora-mqtt-daemon.py -
Cron job - Add a new con job, e.g.,
/etc/cron.d/miflora, execute every 5 minutes*/5 * * * * root python3 /path/to/miflora-mqtt-daemon.py > /dev/null
Integration
Data will be published to the MQTT broker topic "miflora/sensorname" (names configurable).
An example:
{"light": 5424, "moisture": 30, "temperature": 21.4, "conductivity": 1020, "battery": 100}
This data can be subscribed to and processed by other applications, like Home Assistant or openHAB.
Enjoy!
Disclaimer and Legal
Xiaomi and Mi Flora are registered trademarks of BEIJING XIAOMI TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
This project is a community project not for commercial use. The authors will not be held responsible in the event of device failure or other damages.
This project is in no way affiliated with, authorized, maintained, sponsored or endorsed by Xiaomi or any of its affiliates or subsidiaries.